Video Assisted Thoracic Surgery
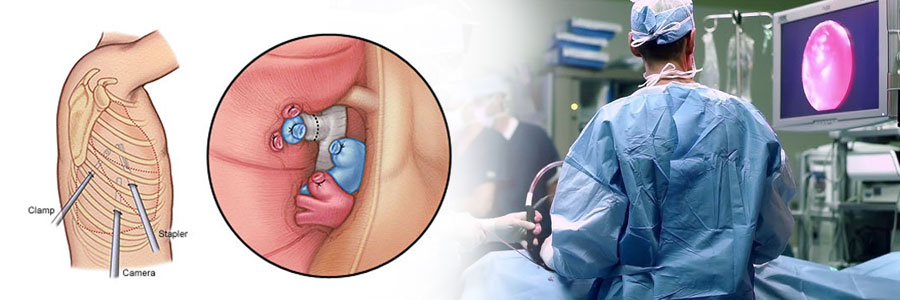
Video-Assisted Thoracic Surgery (VATS) is a minimally invasive surgical technique used to diagnose and treat diseases of the chest, including the lungs, esophagus, and other thoracic organs. VATS involves the use of a small camera (thoracoscope) and special surgical instruments that are inserted through small incisions in the chest. The camera provides real-time video of the inside of the chest cavity, allowing the surgeon to perform complex procedures with greater precision and less trauma to the patient compared to traditional open surgery.
Key Features of VATS:
- Minimally Invasive: VATS requires small incisions (typically 1 to 3) that are about 1-3 cm in length, rather than the large incision used in traditional open surgery.
- Use of a Thoracoscope: A thin, flexible tube with a camera on the end (thoracoscope) is inserted into the chest. The camera transmits video images to a monitor, which the surgeon uses to guide the procedure.
- Specialized Instruments: Small, specialized surgical instruments are used to perform the necessary procedures through the tiny incisions, allowing for precision without the need for opening the rib cage.
Indications for VATS
VATS is used to treat a variety of thoracic conditions, including:
- Lung Cancer: VATS can be used for lung lobectomy (removal of a lobe of the lung) or wedge resection to remove early-stage lung cancer.
- Pleural Effusion: Removal of excess fluid in the pleural space or pleurodesis (sealing the pleural space to prevent fluid buildup) can be done using VATS.
- Biopsies: Lung, pleural, or mediastinal tissue biopsies for diagnosing diseases such as cancer, infections, or interstitial lung disease.
- Mediastinal Tumors: Removal of tumors in the mediastinum (the area between the lungs).
- Infections or Abscesses: Treating infections or abscesses in the chest or lungs.
Benefits of VATS
- Less Pain: Smaller incisions mean less pain compared to open thoracic surgery.
- Faster Recovery: Patients typically experience shorter hospital stays and quicker recovery times.
- Reduced Scarring: Smaller incisions result in less noticeable scars.
- Lower Risk of Complications: Reduced risk of complications such as infections, blood loss, and post-operative lung issues.
- Shorter Hospital Stay: Patients can usually leave the hospital sooner compared to traditional surgery.
