Lobectomy
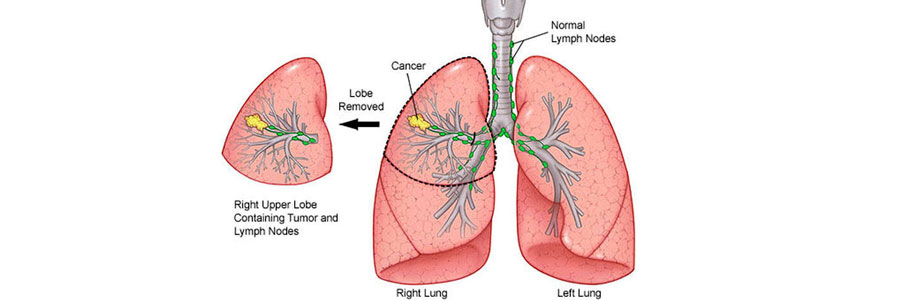
Lobectomy refers to the surgical removal of one lobe of the lung. The human lungs are divided into lobes—three in the right lung (upper, middle, and lower) and two in the left lung (upper and lower). Lobectomy is typically performed to treat conditions affecting a specific lobe, most commonly lung cancer, but it is also used for conditions such as infections, trauma, or benign tumors.
Indications for Lobectomy
Lobectomy is often indicated in the following situations:
- Lung Cancer: This is the most common reason for lobectomy. If a tumor is localized within one lobe, removing the entire lobe can offer the best chance of eliminating the cancer.
- Benign Lung Tumors: Some non-cancerous tumors may need to be removed if they cause symptoms or have the potential to become malignant.
- Severe Lung Infections: Conditions like lung abscesses, tuberculosis, or chronic infections may require the removal of a damaged lobe.
- Bronchiectasis: A chronic condition where parts of the airways become widened and damaged, leading to recurrent infections.
- Trauma: Severe lung injuries sometimes necessitate removing a damaged lobe.
- Congenital Lung Malformations: In children or adults with congenital abnormalities affecting lung development, lobectomy can be performed to improve breathing and lung function.
Benefits of Lobectomy
- Curative Potential: Lobectomy can be curative for patients with early-stage lung cancer or localized infections and diseases.
- Improved Lung Function: Removing damaged or diseased lung tissue allows the remaining healthy lung tissue to function more efficiently.
- Symptom Relief: Patients with infections, bronchiectasis, or other conditions often experience significant symptom improvement after lobectomy.
