Total Arterial Revascularisation
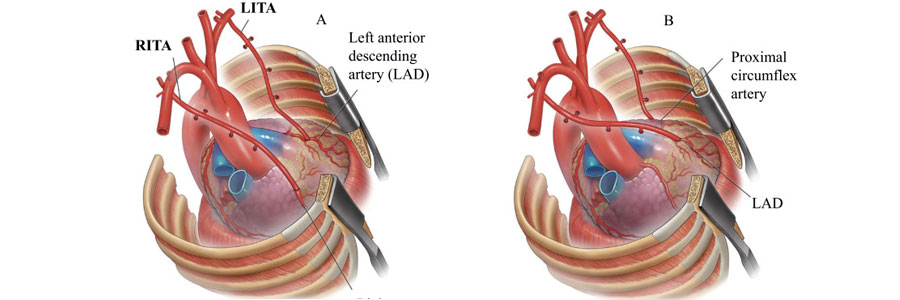
Total Arterial Revascularization (TAR) is a surgical technique used in coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) where only arteries, rather than veins, are used to bypass blocked coronary arteries and restore blood flow to the heart. The goal of TAR is to provide longer-lasting and more durable grafts compared to the traditional use of both veins and arteries in bypass surgery.
Key Features of Total Arterial Revascularization:
1. Arteries Used:
- Internal Mammary Arteries (IMA): Usually the left and sometimes the right internal mammary arteries are the most commonly used arteries because of their long-term patency (ability to stay open).
- Radial Artery: The artery from the forearm (radial artery) can also be used as a graft.
- Gastroepiploic Artery: Sometimes, this artery, which is located in the abdomen, can be utilized, although it is less commonly used.
2. Advantages of Using Arteries:
- Superior Long-term Patency: Arterial grafts have better long-term outcomes than vein grafts because arteries are more resistant to atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries).
- Durability: Arteries are able to withstand higher pressure and offer a more stable blood flow to the heart compared to veins, which are less suited to the high-pressure environment of the coronary arteries.
- Reduced Risk of Reoperation: Because arterial grafts tend to remain open longer, the risk of needing another bypass surgery in the future is lower compared to using vein grafts.
3. Arterial Grafting vs. Vein Grafting:
- In traditional CABG, the saphenous vein from the leg is often used in combination with an artery (usually the left internal mammary artery). While this can be effective, vein grafts have a higher chance of narrowing or becoming blocked over time.
- Total arterial revascularization avoids this problem by using only arteries, which tend to stay open longer.
Benefits of Total Arterial Revascularization:
- Improved Long-term Survival: Studies show that TAR may offer improved survival rates over traditional vein-based grafts.
- Lower Rate of Recurrent Heart Disease: Because arterial grafts stay open longer, patients have a lower risk of future heart attacks or need for repeat surgery.
- Better Blood Flow: Arterial grafts can better handle the pressure and flow demands of the heart's circulation.
