Intracardiac Repair for ASD
Intracardiac Repair for ASD (Atrial Septal Defect) is a surgical procedure to close a hole in the wall (septum) between the two upper chambers of the heart (the atria). ASD is a congenital heart defect that can cause abnormal blood flow between the left and right atria, leading to various complications if left untreated, such as heart failure, arrhythmias, and pulmonary hypertension.
What is an Atrial Septal Defect (ASD)?
- An Atrial Septal Defect is a hole in the atrial septum, the wall that separates the left and right atria. This defect allows oxygen-rich blood from the left atrium to mix with oxygen-poor blood in the right atrium.
- Over time, this can cause increased blood flow to the lungs and strain on the right side of the heart, potentially leading to heart failure and other complications.
Types of ASD:
- Secundum ASD: The most common type, located in the center of the septum.
- Primum ASD: Located near the lower part of the atrial septum and often associated with other heart defects.
- Sinus venosus ASD: A rare type located near the upper part of the septum, close to where the large veins enter the atria.
- Coronary sinus ASD: A rare defect involving the coronary sinus, a vein that collects blood from the heart muscle.
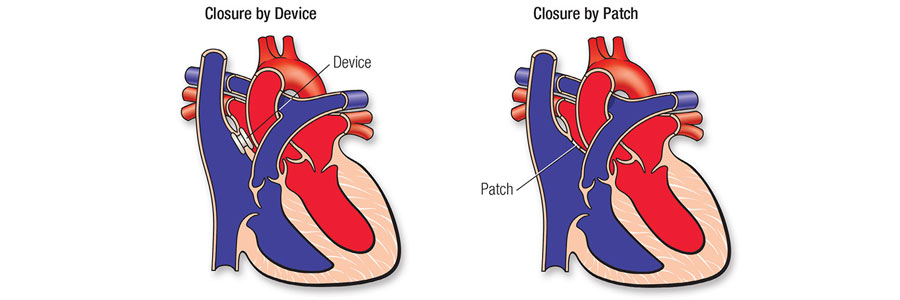
Purpose of Intracardiac Repair:
Intracardiac repair is performed to close the ASD and restore normal blood flow through the heart. This surgery is usually recommended for large or symptomatic ASDs that cannot close on their own or be treated using less invasive procedures, such as catheter-based closure.
Benefits of Intracardiac Repair:
- Restores normal blood flow: Prevents the abnormal mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
- Prevents complications: Reduces the risk of complications such as heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, and arrhythmias.
- Improves quality of life: Many patients experience significant improvement in symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and exercise intolerance.
