Coarctation Surgery
Coarctation surgery refers to surgical procedures aimed at correcting coarctation of the aorta, a congenital condition where a segment of the aorta is narrowed, resulting in restricted blood flow. This narrowing typically occurs just distal to the left subclavian artery, often leading to increased blood pressure in the upper body and reduced blood flow to the lower body. Coarctation of the aorta can lead to various complications, including hypertension, heart failure, and organ damage if left untreated.
Purpose of Coarctation Surgery
The primary goal of coarctation surgery is to relieve the obstruction in the aorta, restoring normal blood flow and reducing the risk of associated complications. Surgical intervention can:
- Improve blood flow to the lower body.
- Normalize blood pressure.
- Prevent complications such as heart failure, stroke, or aortic rupture.
Indications for Coarctation Surgery
Surgery is indicated in patients with:
- Significant coarctation: Patients with a substantial narrowing of the aorta that results in high blood pressure or reduced blood flow to vital organs.
- Symptoms: Such as headaches, leg cramps, or signs of heart failure.
- Hypertension: Particularly in children and young adults who do not respond to medical management.
- Associated congenital heart defects: If present, these may also necessitate surgical intervention.
Types of Coarctation Surgery
There are several surgical approaches to correct coarctation of the aorta, including:
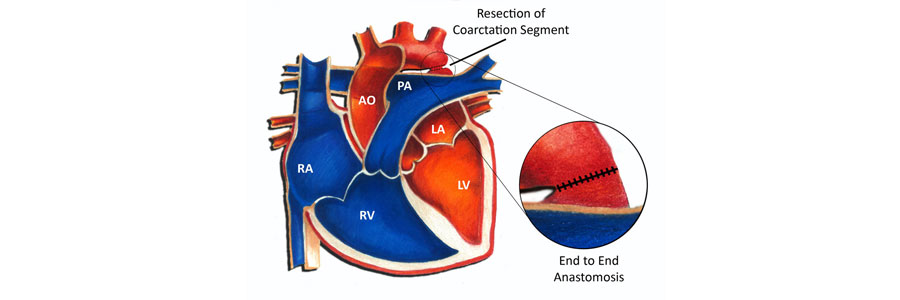
- Resection and End-to-End Anastomosis: This is the most common surgical technique. The narrowed segment of the aorta is excised (resected), and the two ends of the aorta are sewn back together (anastomosed).
- Subclavian Flap Aortoplasty: In this technique, a portion of the left subclavian artery is used to create a flap that covers the narrowed section of the aorta. This is particularly useful in younger patients where growth is a consideration.
- Patch Aortoplasty: A patch made from synthetic material or the patient’s own tissue is placed over the narrowed segment to enlarge it. This method can be used in cases where the aorta is too narrow to simply resect.
- Stenting (Endovascular Approach): In some cases, a stent may be placed to open the narrowed area. This approach is less invasive and can be performed in adults or older children.
Benefits of Coarctation Surgery
- Restoration of Blood Flow: Surgery effectively restores normal blood flow to the body, alleviating symptoms and complications.
- Improved Quality of Life: Patients often experience significant improvements in their overall health and well-being post-surgery.
- Prevention of Long-term Complications: Timely surgical intervention can prevent serious long-term issues associated with untreated coarctation.
